Preview this deck
Delian League
Front
Active users
2
All-time users
2
Favorites
0
Last updated
9 months ago
Date created
Jun 24, 2020
Cards (6)
Greek Government
(4 cards)
Delian League
Alliance between Athens and many of its allied cities following the first attempted invasion of Perisa into Greece. Caused a lot of wealth to flow into Athens and thus contributed to the Athenian "golden age."
Darius I
Commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third Persian King and reigned from 522-486 BCE.
He ruled the empire at its peak, and launched the first First Persian Invasion of Greece, effectively starting the Persian Wars.
Solon
An elected tyrant that abolished slavery, wiped debts clean, and let people vote. He was an Athenian statesman, lawmaker and poet. He is remembered particularly for his efforts to legislate against political, economic and moral decline in archaic Athens.
Unfortunately, his efforts failed (in the short-term), but he is credited for having laid the foundations for Athenian democracy that the Greeks were so famous for.
Salamis
The 4th battle of the Persian War. The Oracle of Delphi told the Greeks to hide in ships, and Themistocles (the general) tricked the Persians into coming into the narrow water straits of Salamis. Became a sea battle w/ Xerxes, and the Greeks won.
Greco Science
(2 cards)
Thale's Intercept Theorem
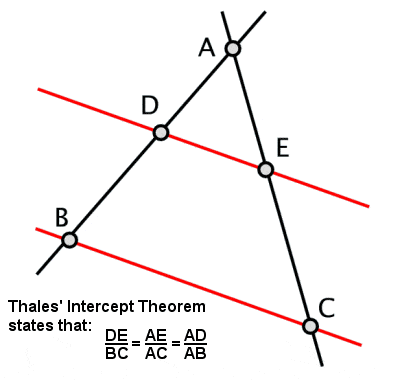
Thales, one of the Seven Sages of Ancient Greece, is usually considered to have been the first to lay down guidelines for the abstract development of geometry, although what we know of his work.
"Thales’ Theorem- if a triangle is drawn within a circle with the long side as a diameter of the circle, then the opposite angle will always be a right angle."
Pythagorean Theorem
The classic right triangle theorem, which says that $$a^2 + b^2 = c^2$$ where \(a\) and \(b\) are legs of the right triangle, and \(c\) is the hypotenuse.



