Cards (18)
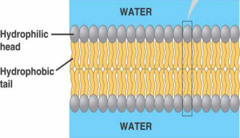
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes,
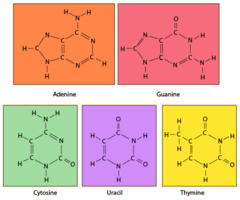
An organic base that contains nitrogen, such as a purine or pyrimidine; a subunit of a nucleotide in DNA and RNA
Biological catalysts
Any of a group of usually synthetic hormones that are derivatives of testosterone, are used promote tissue growth,
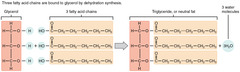
is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.
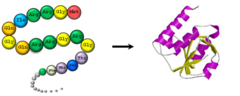
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
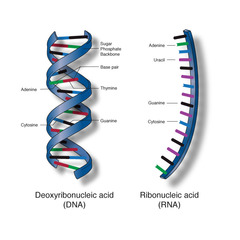
DNA and RNA
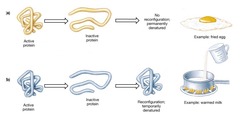
In proteins, a process in which a protein unravels and loses its native conformation,
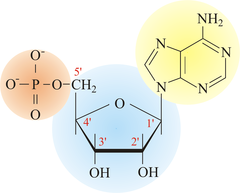
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
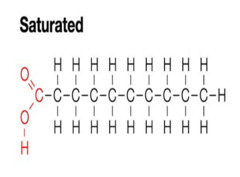
Fats with the maximum number of hydrogens.
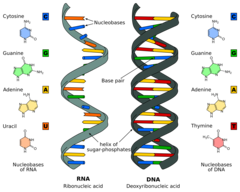
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
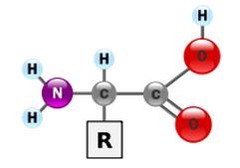
Building blocks of proteins
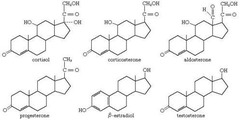
Made of four rings of carbon.
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
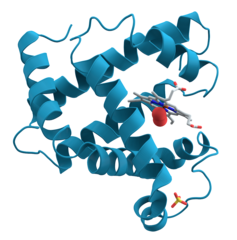
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
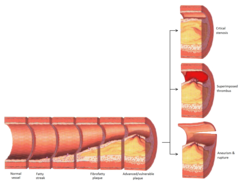
Hardening of the arteries
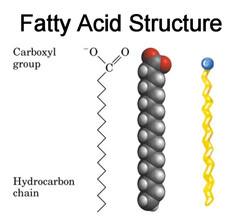
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
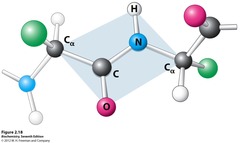
Bonds that connect amino acids.