Section 1
Preview this deck
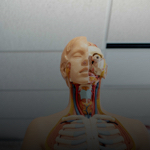
Coronal (Frontal)
Front
Active users
2
All-time users
2
Favorites
0
Last updated
1 year ago
Date created
Mar 1, 2020
Cards (672)
Section 1
(50 cards)
Coronal (Frontal)
This plane divides the body into front and back portions?
Types of bones
Long bones Short bones Irregular bones Sesamoid bones
Meiosis
Special cell division that takes place in the gonads- the chromosome number is reduced from 46 to 23 so when the egg and the sperm unite in fertilization, the zygote will have the correct number of chromosomes
Transverse
This plane divides the body into upper and lower portions?
Voluntary muscle
Skeletal muscles
A long bone is composed of
An irregular epiphysis composed of spongy bone diaphysis composed of compact bone
Functions of the skeletal system
Support Movement Blood cell formation Protection of internal organs Detoxification Provision for muscle attachment Mineral storage (calcium and phosphorus)
Distal
This means that a body part is further away from the center of the body
Organs
Tissues are group in what?
Epidermal cells contain what protein pigment
Melanin
Skin
The largest organ of the body
Apocrine sweat glands
Found in the armpits and groin area- cell debris attacts bacteria and the presence of bacteria on the skin results in body odor
Tissue
Group of cells that act together to perform a specific function
Epithelial Cells
Cover, line and protect the body and its internal organs
Nucleus
Contains DNA and ribosomes which are important in the synthesis of proteins
Layers of the Epidermis
Stratum Corneum, Stratum Lucidum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Germinativum (basale and spinosum) where mitosis occurs
Meiosis
This has the same phases as Mitosis, however they happen twice and this is specific for sperm and ovum
Systems
Organs are grouped into what?
Histology
The study of tissues
Cell
The basic unit of life and the building block of tissues and organs
Proteins
Include enzymes that regulate all chemical reactions within the body
Sagital
This plane divides the body into R and L portions
Tissues
This is a group of cells that work together to perform a specific function?
Osteoblasts
Cells that form compact bone
Prophase
Chromatin thickens into chromosomes, nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, centrioles move to either side, and chromosomes are moved around
Sebaceous glands
Release an oily secretion (sebum) through the hair follicles that lubricates the skin and prevents drying
Muscle Tissue
Have the ability to contract or shorten; classified as voluntary or involuntary
Mitosis
Necessary for growth and repair. DNA is duplicated and distributed evenly to two daughter cells
Dermis
Underlying layer of connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve ending and the associated skin structures- rests on the subcutaneous tissue
Caudal
This means closer to the tail
Metaphase
Spindle moves to the center of the cell and chromosome pairs align along the center
Anaphase
Chromosomes pairs separate to ends of cell
Two layers of skin
Epidermis and Dermis
The four fundamental tissues
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nerve tissues
Two types of sweat glands
Eccrine and Apocrine
Connective Tissue
The framework of the body, providing support and structure for the organs
Eccrine sweat glands
The most widely distributed glands that regulate body temperature by releasing a watery secretion that evaporates from the surface of the skin
Epidermis
Outermost protective layer composed of dead keratinized epithelial cells
Nerve Tissue
Composed of neurons and connective tissue cells that are referred to as neuroglia
Major body cavities are divided into the
Dorsal and Ventral Cavities
Cytokinesis
This is the splitting of two cells, it begins during anaphase and is completed after telophase
Telophase
Spindle disintegrates, nuclear membranes reform and membranes are pinched
Muscle Skeletal Smooth Nerve Epithelial Connective
Name all 6 tissue groups.
What is produced by holocrine secretion?
Oil
Organisim
This is a complete individual.
Involuntary muscle
Smooth or cardiac muscles
Tissues
Cells are grouped together into what?
Interphase
Cell prepares for division, it replicates DNA and cytoplasmic material (G1, S, G2)
The appendages of the skin
Hair and nails
Proximal
This term means that a body part is closer to the center of the body
Section 2
(50 cards)
atoms make
molecules
Ribs
Consists of 12 paired, 10 true, and 2 floating
Trapezius
This muscle moves the shoulder
Sweat glands
This is associated with homeostatic relationship of thermoregulation and helps to rid the body of waste
Bones
These store minerals and produce blood cells
Exocrin
Sebaceous glands are also known as this
Axial
80 bones vertebral column rib cage sternum skull hyoid
Hyoid bone
This provides attachment for the tongue muscles
tissues make
organs
Pectoral Girdle
Consists of the Scapula and Clavicle
Sebaceous glands
These are connected to hair follicles, secrete through hair pore and inhibit water loss
Pelvic Girdle
Consists of hip bone and sacrum
Temporalis/Masseter
These muscles move the mandible
Vasodialation
Releases heat into the environment to lower body temp
Sebum
Oily mix of lipids and proteins
Keratinized
Most epidermal cells are what?
Epidermis
This is the most superficial layer of the skin. It consists of epithelial cells, does not contain blood vessels.
Eccrine glands (Sweat Glands)
These are not attached to hair follicles that are activated by elevated body temp, located throughout the body, secrete salty solution
Vertebral Column
Consists of 33 vertebrae which include the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral
Pectoralis Major Deltoid Latissimus Dorsi
Move upper arm
Hypodermis (subcutaneous
This is not a layer of skin. It consists of connective tissue which binds skin to muscle. Fat deposits help cushion and insulate.
Spongy Bone
This consists of trabecula which is a network of open spaces filled with red bone marrow. They are light weight, porous and reduces bone weight
Rectus abdominus/External Oblique/and Erector spine
These move the trunk
Epiphysis
Red marrow is found here?
Keratin
This is a waxy protein that also helps to waterproof skin
sweat glands
These are also considered Eccrine or apocrine
Receptors (sensory cells), Control Center (hypothalmus), and effector (sweat glands, blood muscles (shiver)
Name the 3 things involved with negative feedback during thermoregulation
Gluteus maximus
This moves the upper leg
Appenduclar
126 bones pectoral girdle pelvic girdle Appendages
Haversian System
This provides a reservoir for calcium and phosphorus for blood
External and Internal Oblique
Elevate and depress the ribs
Gastrocnemius/Soleus
These extend the foot
Sternocleidomastoid
This muscle moves the head
Thermoregulation
This is the activation of sweatglands and is controlled by negative feed back
cells make
tissues
Diaphysis
Long bones have this?
Appendicular portion
arms legs
Orbicularis Occuli
This closes the eye and draws lips together
Skeletal System
206 bones axial and appendicular
Red marrow
red and white blood cells
Apocrine glands
Secrete oily sebum, located in armpits, feet, groin, and palms. Bacteria feed off of the sweat expelling and aromatic fatty acid also known as body odor.
Sebaceous glands
This secretes sebum to waterproof skin
Dermis
This lies directly below the epidermis, consists of connective tissue, contains blood vessels, sensory receptors, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. Also contains elastin and collagen
Integumentary System
This consists of skin, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, hair, and nails and manufactures Vit D
Bicep brachii Tricep brachii
Move lower arm
Sternum
manubrium corpus sterni xiphoid process
Stratum Basal
This is the deepest portion of the Epidermis. It is a single layer of cells and has continual cell division
Compact bone
This consists of tightly packed cells. They are strong, dense, and rigid. And they contain Haversian canals that run vertically and are surrounded by concentric circles of Lamellae
molecules make
cells
Skull
Includes Cranium, Facial bones, ossicles (bones in middle ear), hyoid bone
Section 3
(50 cards)
parathyroid hormone
takes calcium from the bones to make it available for the blood
endocrine
pituitary thyroid pancreas ovaries
integumentary
hair skin nails
nucleus
contains genetic information...and DNA is here
vestibulocochlear nereve
hearing and balance
cranial nerves
12 Pairs
hypertonic, isotonic, hyoptonic
differentiation
cells become specialized to do something
digestive
mouth esophogas stomach intestines
urinary
kidneys ureters urethra bladder
trochlear nerve
eye movement
pituitary gland regulated
hypothalamus
adrenal gland
Epinephrine & Norepinephrine - Aldosterone - a mineralcorticoid, helps kidneys conserve sodium and excrete potassium, maintaining blood pressure Cortisol - keeps blood glucose levels stable, stress hormone Adrenal Sex Hormones - androgens (male) and estrogens (female)
main funcitons of red blood cells
transport Oxygen to body removes Carbon Dioxide out of body
fibroblasts
produce fibers and collagen
abducens nereve
eye movement
smooth muscles
autonomic nervous system
anemia
few red blood cells
Anteriror pituitary Adenohypophysis Tropic Hormones
Prolactin or PRL - Growth hormone or GH - Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - Thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH - Luteinizing hormone or LH - Follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH - FLAT PIG
Diapraghm
separates thoracic and abdominol cavitys
peritoneum
surrounds cavity around abdimonal cavity
centrosome
helps with cell divison
visceral
covers an organ
circulatory
heart blood vessels blood
macrophages neutrophiles
two types of WBC's
olfactory nerve
smell
cytoplasm
ribosomes here
optic nerve
vision
PNS
nerves to body
skeletal
bones ligaments cartilage
parietal
covers an area around an organ
lymphatic
IMMUNE SYSTEM fights infections
nervous
brain spinal cord
Axial portion
head neck trunk
rough er
ribosomes located
pancreas
behind stomach stimulates liver to break down glycogen
skeletal muscles
somatic nervous system Afferent/Sensory nerves Efferent/Motor Nerves
pleura
lungs
What cell structure is missing from blood cells?
nucleus
calcitonin
regulates blood calcium level
cytokinesis
cytoplasmic divison
CNS
brain spinal cord
neurotransmitter that stimualtes muscles to contract
acetylcholine
mitosis
nuclear division prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinsis
thyroid gland
controls metabolism
oculomotor nerve
eye movement
spinal nerves
31 Pairs
posterior pituitary neurohypophysis
oxytocin ADH (Antidiuretic hormone)
trigemenal nerve
muscles for chewing
reproductive
ovaries testes
Section 4
(50 cards)
how is blood supplied to the myocardium (heart muscle)
coronary arteries
where do the superior and inferior vena cava veins empty?
into the right atrium of the haert
epidcardium
most superficial layer
respiratory system
nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi lungs
what does the cortisol do
reduce inflammation raises blood sugar level inhinbits release of histamine
where are all formed elements of blood formed
in the red bone marrow
leukocytes
white blood cells
ECG (electrocardiogram)
hearts intrinsic beat by the sinoatrial node thru the myocardium
salivary glands
3
left atrium and left ventricle
recieves blood from pulmonary veins
external respiration
exchange of gases between the atmosphere and blood thru aveoli (*STARTS EXTERNALLY)
erythrocytes
red blood cells
endocrine system location of main glands
pineal, pituitary, hypothalamus, parathryroid, thymus, testes, ovaries, pancreas, adrenals
respiratory system controlled by
medulla oblongata
systemic arteries
being with aorta, and branch to all parts of hte body
pituitary gland
master gland
why are hormones of the adenohypohysis (anterior pituitrary) also called tropic hormones
because they act mainly on other endocrine glands
valves between the atria and ventricles
tricupsid (right side of heart) bicupsid (left side of heart)
pericardial sac
surrounds heart and helps prevent overfilling
how is the pituitary gland attatched to the hypothalamus
infundibulum
contraction phase of the cycle
systole
ECG measure the
electrical activity that precedes the contraction and relaxtion evenets of the myocardium
what side of the heart is the bicupsid valve on
left side
right atrium and right ventricle
pumps blood into the pulmonary arteries
what side of the heart is the tricupsid valve on
right side
where does blood drain from and to
from the myocardium direectly into the right atrium thru the corony sinus
pulmonary circuit
deoxygenated blood heart to the lungs and back Carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs and back
white blood cells active in phagocytosis
neutrophiles and monocytes
where does the heart send blood to
lungs for oxygenation through the pulmonary circuit, and the remainder through the systemic circuit
3 layers of heart Out to In
epicadium myocardium endocardium
systemic circulation
Oxygenated Blood Lungs to body tissue carries oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the body tissues
endocardium
epithelium covering inner surfaces including heart valves
where does the liver get its blood from
hepatic artery brings oxygen-rich blood from the heart. hepatic portal vein brings blood rich in digested nutrients from the intestine.
digestive system (alimentary canal)
mouth pharynx esophagas stomach small intestine large instestine rectum anus
myocardium
musclar wall of heart
exhalation
passive process where the lungs recoil as the respiratory muscles relax and thorax decreases in size
cortisol realased from
adrenal cortex
cappillaries
smallest of vessels exchanges take place between blood and surrounding tissues, exchanging water, nutrients, and waste products
cardiac cycle
end of one ventricular contracton to the end of the next contraction
platelets
blood clotting
inhalation
contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic cavity to draw air into lungs
relaxation phase of the cycle
diastole
smallest arteries are called what
arterioles
regulates of blood ph
carbon dioxide
internal respiration
exchange of gases between blood and body cells (IN THE BODY COMLETELY)
3 parts of whole blood
plasma leukocytes erythrocytes
white blood cells that form antibodies
lymphocytes
arteries
carry blood away from the heart
accessory organs of digestive system
liver pancreas gallbladder
what is the endocrine systems main function
production of hormones!
Section 5
(50 cards)
what day of the cycle does the LH get released
day 14
secretes the progesterone and estrogen
corpus luteum
intestinal flora
the large intestine has an abundent amount of
functional unit of kidneys
nerphons
if the corpus luteum does not get fertilized
it would degenerate and mentstration begins
sperm develop
seminiferious tubules of each teste
peritoneum
surrounds cavity around abdimonal cavity -parietal & visceral peritoneums
pleura
lungs
skeletal muscles are controlled by the
somatic nervous system
cytokinesis
cytoplasmic divison
bolus
a ball of food
Erythropoiesis?
red blood cell formation
nutrients go from small intestine for decontamination
liver
fibroblasts
produce fibers and collagen
which enzymes act on food in the small intestine
pancrease and bile from the liver
cytoplasm
ribosomes here
Function male and female reproductive organs
gametes (sex cells) hormones (under control of tropic hormones in pituitary gland)
differentiation
cells become specialized to do something
digestion and absopriton of food happen
in the small intestine
smooth muscles are controlled by the
autonomic nervous system
large intestine 5 portions
ascending colon transverse colon descending colon sigmoid colon rectum
What is the relationship between sarcomeres and muscle cells?
Sacrocmeres - Myofibrils- Muscle Cell
villi
small finger like projections increase surface area of instestines
ejaculatiojj pathway
vas deferens ejaculatory duct urethra
glands that produce semen
seminal vesicles prsotate gland bulbourethral (copwers) gland
Hypotonic Hypertonic Osmosis
cells are filled with ions (K+, Na ions) water outside the cells burst open When you eat Sodium** the cell is lacking ions/solutes water outside the cell cell shriveled/deprived When you don't drink water** water likes to diffuse to area of high concentration where the solutes are
parietal
covers an area around an organ
small intestine 3 major regions
duodenum jejunum ilieum
final product of the kidney
urine
centrosome
helps with cell divison
what is it called when the food gets churned and broken down in the stomach
chyme
breaks down food in the stomach
hcl
lymphatic
IMMUNE SYSTEM fights infections
rough ER
ribosomes located here
filters the blood
kidneys
what does the large intestine do
resorb water and stores and elimiantes undigested food....
glomerulus in bowmans capsule of nerphon
this is where the acgtual filtration process happens in the kidneys
why do eggs in the ovarian follies ripen?
they are under control of the FSH
Muscles produce contraction due to the sliding action of:
filaments slide together by using energy supplied by ATP.
ureters
transport urine to the bladder
urine stored
urinary bladder
what stimulates development of the endometirum
progetorone and estrogen
intertitial cells between seminiferous tubues prouduce what
testosterone
LH gets released from the pituitary gland
ovulation is stimulated
mitosis
nuclear division prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinsis
sperm stored and done being produced
epidiymis of each testi
opening for defication
anus
testicular activity under control of
FSH...regulates sperm production LH...stimulates intersitial cells to produce testosterone Anterior Pituitary, Tropic, A
urinary system
2 kidneys 1 urethra 1 urinary bladder 2 ureters
preperation for the endometirum of the uterus for pregnancy
estrogen
Section 6
(50 cards)
trigemenal nerve
muscles for chewing
where does the heart send blood to
lungs for oxygenation through the pulmonary circuit, and the remainder through the systemic circuit
trochlear nerve
eye movement
pericardial sac
surrounds heart and helps prevent overfilling
where is sperm stored and done being produced
in the epidiymis of each testi
how many pairs of salivary glands are there
3
what is testicular activity under control of
2 anterior pituitary hormones FSH...regulates sperm production LH...stimulates intersitial cells to produce testosterone
what does the cortisol do
reduce inflammation, raises blood sugar level, and inhinbits release of histamine
abducens nerve
eye movement
how many pairs of spinal nerves are ther
31
calcitonin
regulates blood calcium level
where is cortisol realased from
adrenal cortex
right atrium and right ventricle
pumps blood into the LUNGS/pulmonary arteries
neurotransmitter that stimualtes muscles to contract
acetylcholine
small intestine 3 major regions
duodenum, jejunum, ilieum
which enzymes act on food in the small intestine
pancrease and bile from the liver
ANTERIOR pituitary hormones-- adenohypophysis
acryonm to remember: FLAT PIG FSH, LH, ACH, TSH, PRL, GH
main function of male and female reproductive organs
production of gametes (sex cells) and production of hormones (under control of tropic hormones in pituitary gland)
where are all formed elements of blood formed
in the red bone marrow
intestinal flora
the lrage intestine has an abundent amount of bacteria called intestinal flora
why do eggs in the ovarian follies ripen?
they are under control of the FSH
glands that produce semen
seminal vesicles prostate gland bulbourethral (cowpers) gland
adrenal gland
Epinephrine & Norepinephrine - Aldosterone - a mineralcorticoid, helps kidneys conserve sodium and excrete potassium, maintaining blood pressure Cortisol - keeps blood glucose levels stable, stress hormone Adrenal Sex Hormones - androgens (male) and estrogens (female)
intertitial cells between seminiferous tubues prouduce what
testosterone
where does the liver get its blood from
1. The hepatic artery - brings oxygen-rich blood from the heart. 2. The hepatic portal vein - brings blood rich in digested nutrients from the intestine.
regulator of blood Ph?
carbon dioxide
valves between the atria and ventricles
tricuspid (right side of heart) bicuspid (left side of heart)
pancreas
very large gland behind your stomach... stimulates liver to break down glycogen
how is blood supplied to the myocardium (heart muscle)
by the coronary arteries
glomerulus in bowmans capsule of nephron
this is where the actual filtration process happens in the kidneys
large intestine 5 portions
ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and the sigmoid colon , and then the rectum
parathyroid hormone
takes calcium from the bones to make it available for the blood
where does blood drain from and to
from the myocardium directly into the right atrium thru the corony sinus
What cell structure is missing from blood cells?
nucleus
how is the pituitary gland regulated?
the hypothalamus
what breaks down food in the stomach
HCl
where do nutrients go from small intestine for decontamination
the liver!
what is the respiratory system controlled by
the medulla oblongata
left atrium and left ventricle
recieves blood from PULMONARY VEINS veins
white blood cells that form antibodies
lymphocytes
ejaculation pathway
vas deferens ejaculatory duct urethra
how many pairs of cranial nerves are there
12
vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance
3 parts of whole blood
plasma, leukocytes, erythrocytes
why are hormones of the adenohypohysis (anterior pituitrary) also called tropic hormones
because they act mainly on other endocrine glands
POSTERIOR pituitary hormones (neurohypophysis)
oxytocin and ADH
how is the pituitary gland attatched to the hypothalamus
infundibulum
where do the superior and inferior vena cava veins empty?
into the right atrium of the haert
where does sperm develop
in the seminiferious tubules of each teste
white blood cells active in phagocytosis
neutrophiles and monocytes
Section 7
(50 cards)
what secretes the progesterone and estrogen
corpus luteum
Lateral is
AWAY from the MIDLINE
Superior is
ABOVE
Distal is
FURTHER away from the point of attachment
MEIOSIS
Cells division that takes place in the gonads (ovaries and the testes)
Connective Tissue is the framework of?
The body, providing support and structure for the organs
The EPIDERMIS is the
Outermost protective layer of dead keratinized epithelial cells
What are the 4 Fundamental Tissues of the Human Body?
Epithelial Tissue Connective Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Medial is
TOWARD THE MIDLINE
Epithelial Cells do what?
Cover, line, and protect the body its internal organs
Where does the DERMIS rest?
On the subcutaneous tissue that connects the skin to the superficial muscles
What is the anatomic position?
The body is erect, feet slightly apart, the head is held high, and the palms of the hands are facing forward
Tissue
Group of cells that act together to perform specific functions
What is the basic unit of life?
A CELL!
Dorsal Body cavity
Cranial Spinal Nerves
Muscle tissue is classified as?
Voluntary Muscles and Involuntary Muscles
what happens when the LH gets released from the pituitary gland
ovulation is stimulated
What does a nucleus contain?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribosomes
What muscles are involuntary?
Smooth Muscles
The DERMIS is the
Underlying layer of connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and the associated skin structures
Frontal Section
CORONAL PLANE
Levels of the Body
atoms molecules cells tissues organs organ systems
What is a neuroglia?
A connective tissue nerve cells
process of MEIOSIS
chromosome reduced from 46 to 23
Muscle tissue have the ability to?
Contract or shorten
what initiates preparation for the endometirum of the uterus for pregnancy
the estrogen
Truculent
Eager or quick to argue or fight; aggressively defiant
MITOSIS
Growth and repair
process of MITOSIS?
DNA is duplicated Two daughter cells
proteins
Enzymes that regulate all chemical reactions within the body
Who is the building block of tissues and organs?
A CELL!
Cross-Section
TRANSVERSE PLANE
Ventral Body cavity
orbits nasal oral thoracic Abdominopelvic cavities
Proximal is
CLOSER to the point of attachment
what stimulates development of the endometrium
progetorone and estrogen
MITOSIS occurs in what layer of the skin
The innermost layer Stratum Germinativum
Nerve Tissue is composed of?
Neurons and connective tissue cells
What is the largest organ of the body?
THE SKIN!
When the egg and sperm unite in fertilization the zygote will have the correct number of chromosomes
MEIOSIS
Stratum Germinativum consists of what?
Stratum Spinosum Stratum Basale
Histology is the study of what?
TISSUES!
Job of a ribosome
Synthesizes proteins
Inferior is
BELOW
What are the two layers of the skin?
EPIDERMIS and the DERMIS
if the corpus luteum does not get fertilized what happens
it would degenerate and mentstration begins
Anterior is
FACING FORWARD
What muscles are voluntary?
Skeletal Muscles
Posterior is
TOWARD THE BACK
Sagittal Section
MEDIAN PLANE
What are the layers of the EPIDERMIS from the OUTER layer to the INNER layer
Stratum Corneum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Spinosum Stratum Basale
Section 8
(50 cards)
Sacrum bone
Lower back Bone Between hip bone
Sebaceous glands release
Oily secretion Through hair follicles that lubricates the skin and prevents drying
Oils are produced by
Holocrine Secretion
Muscle that produces the opposite movement
ANTAGONIST
What are the 2 types of sweat glands?
Eccrine and Aprocrine
Energy supplied by ATP, actin and myosin filaments slide together to produce
CONTRACTION
Sebaceous glands are susceptible to
Clogged and attracted to bacteria Particularly during adolescence
Aprocine Sweat gland secretion
cytoplasm
(T/F): Skeletal muscles work in pairs?
TRUE!
UPPER portion APPENDICULAR SKELETON
Pectoral of Shoulder Girdle Clavicle Scapula Upper Extremity
Needs to be present for a muscle cell to contract
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Nervous stimulation from motor neurons
Release of calcium ions from the sacroplasmic reticulum
Sacromere
Functional unit of a muscle cell Sarcomeres- Myofibrils- Muscle Cell
The body's framework consists of
Bone Cartilage Ligaments Joints
Skeletal muscles are also called what type of muscles?
VOLUNTARY MUSCLES! Because they are under CONSCIOUS control
APPENDICULAR SKELETON
Girdles Limbs
LOWER EXTREMITY of APPENDICULAR SKELETON
Femur (thigh bone) Patella (knee) Tibia Fibula Metatarsals (foot) Phalanges (toe bones)
Calcium ions attach to inhibitory proteins on what type of filaments?
On the ACTIN filaments within the cell, moving them aside so that cross-bridges can form between ACTIN and MYOSIN filaments
LOWER portion APPENDICULAR SKELETON
PELVIC GIRDLE
Muscle that executes a given movement
PRIME MOVER
Vertebral Column Smallest to largest
Cervical Vertebrae 7 Thoracic Vertebrae 12 Lumbar Vertebrae 5
Synergist
Other muscles that decide to work in cooperation with the prime mover
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
14 FACIAL bones 14 CRANIAL bones 28 total
Arm Bones
Humerus Radius (forearm) Ulna (forearm) Carpals (wrist) Metacarpals (hands) Phalanges (fingers)
Cell debris from the Aprocine Sweat gland
Attracts bacteria Bacteria on the skin results in body odor.
A typical long bone has a what?
IRREGULAR Epiphysis at each END Composed of Spongy aka CANCELLOUS bone Shaft or a Diaphysis composed of Compact bone
Os Coxae is fused with
Ilium Ischium Pubis
Melanin protects against
Radiation from the sun
AXIAL SKELETON VERTEBRAE COLUMN
33 CERVICAL vertebrae THORACIC vertebrae LUMBAR vertebrae SACRAL vertebrae COCCYGEAL vertebra aka the tail bone
Hemopoiesis
Blood Cell Formation
The Final portion of the AXIAL SKELETON
THORAX (rib cage) STERNUM 12 pair of RIBS
Hair and nails are composed of
KERATIN
Cross-bridges form between
ACTIN filaments MYOSIN filaments
Calcium and Phosphorus helps with the Skeletal Systems?
Mineral Storage
Extensors
INCREASE the angle
Appendages of the skin
Hair and Nails
Sacral vertebrae is fused to form
Sacrum
Pelvic Girdle is also known as the
"OS COXAE"
Eccrine Sweat gland
Regulates body temperature By releasing a watery secretion that evaporates from the surface of the skin MOST WIDELY distributed
Epidermal cells contain a protein pigment
MELANIN
Epidermal Cells move from what?
1. The deepest layers to the superficial layers 2. They move away from their blood and nutrient supply 3. Then they dehydrate and die
Aprocrine Sweat gland
Armpits Groin area
What happens to OSTEOBLASTS when they become fixed in the dense bone matrix
Stop dividing but continue to maintain bone tissues as osteocytes
Muscle contraction results
Sliding together of actin and myosin filaments within the muscle cell or fiber
Functions of the Skeletal system
Support Movement Blood Cell Formation Protection of Internal Organs Detoxification Provision for muscle attachment Mineral Storage
Dermis is composed of
Fibrous connective tissue with blood vessels Sensory nerve endings Hair follicles Glands
muscle cell consists of
MYOFIBRILS
Cells that form compact bone a
Osteoblasts
Muscles produce movement
Contracting in response to nervous stimulation
Flexors
REDUCE the angle at the joint
Section 9
(50 cards)
The NS is divided into how many systems?
Central Nervous System (CNS Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The NS enables us to
Think Reason Remember Carry out other abstract activities
Organs/gland that make up the ENDOCRINE GLAND
Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Pineal Ovaries in females Testes in males Pancreas, aka Islets Parathyroid Adrenals
Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) of the pituitary hormone
OXYTOCIN - labor hormone ANTIDIURETIC ADH regulates and balances the amount of water in your blood Tells the kidneys how much water to conserve
(T/F): Other organs, such as the stomach, small intestine, and kidneys, produce hormones as well
TRUE!
There is a total of how many SPINAL Nerves?
31 pairs
All actions of the NS depend on?
The Transmission of nerve impulses over neurons or nerve cells
Steroid hormones
Direct effect on the DNA of the nucleus
Pituitary Gland is attached to
Hypothalamus (infundibulum)
Non-steroid hormones
(Some) Are PROTEIN hormones
Sensory impulses ENTER
DORSAL horns
The PNS consists of
ALL nerves that transmit information to and from the CNS Cranial & Spinal Nerves Communication lines between the CNS & the rest of the body
List the other important ENDOCRINE glands
Thyroid Parathyroids Adrenals Pancreas Gonads, which include the ovaries and the testes
Medulla Oblongata
respiration heart rate is part of the Brain Stem
Sensory Afferent neurons transmit nerve impulses
TOWARD the CNS
The NERVOUS SYSTEM consists of what?
The Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerves
NS makes body movements by the skeletal muscles possible by supplying them with
Nerve impulses that cause contraction
Two major group of hormones
Steroid Non-steroid hormones
Most hormones affect cell activity
Alternating the rate of protein synthesis
Hormones of the Adrenohyopphysis are called?
TROPIC hormones because they act mainly on other endocrine glands
Ventral
Bottom
The HYPOTHALAMUS governs the
PITUITARY gland and is in turn controlled by the feedback of hormones in the blood
What are the 3 major parts of the BRAIN?
The Cerebrum The Cerebellum The Medulla Oblongata
Abductors
Draw a limb AWAY from the midline
Why are widely distributed ENDOCRINE glands group together?
Because the main function of each gland is the production of hormones
Hormones released during stress
Adrenal Cortex Hypothalamus Anterior and Posterior Pituitary
There is a total of how many CRANIAL Nerves?
12 pairs
Many protein hormones remain where
At the cell surface and act through a second messenger ADENONSINE MONOPHOSPHATE (AMP)
Formed elements of the Blood
Erythrocytes (RBC) Leukocytes (WBC) Platelets
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems coordinate and control...
THE BODY, BUT the ENDOCRINE system has MORE long-lasting and WIDE spread effects
List the following TROPIC (adrenohypophysis) hormones
Somatotropin Hormone, STH or Growth Hormone, GH Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone, ACTH Thyroid-stimulating hormone, TSH Follicle-stimulating hormone, FSH Luteinizing hormone, LH
Whole blood consists of
55% PLASMA 45% FORMED ELEMENTS
Motor impulses LEAVE
VENTRAL horns
Two major portions of the pituitary gland
Anterior Lobe (Adrenohypophysis) Posterior Lobe (Neurohypophysis)
What is the role of CORTISOL?
Released from the ADRENAL CORTEX, Raises the blood sugar level, and inhibits the release of histamine
The Nervous system helps us perceive many changes that happen internally and externally in the environment and to respond to those changes
TRUE
The ENDOCRINE system assists in
The NERVOUS SYSTEM in HOMEOSTASIS GROWTH and SEXUAL MATURATION
Dendrites transmits impulses where?
TOWARD the cell body
Functional units of the NS
Neurons or Nerve Cells
Spinal Cord extends
SKULL (foramen magnum) to First or Second LUMBAR REGION
What are the main parts of a neuron?
The Body Axon Dendrites
Dorsal
Top
Hormones
Chemical messengers Control: growth differentiation metabolism of specific target cells
Cerebrum
Movement Sensory Input Biggest part of the brain
Cerebellum
Muscular Coordination Posture Balance 2nd largest part of the brain
Adductors
Draw a limb TOWARD the body
The Axon transmits impulses where?
AWAY from the cell body
Motor Efferent neurons transmit nerve impulses
AWAY from the CNS toward the effector organs muscles glands digestive organs
NS works closely with what gland
ENDOCRINE GLAND (ductless gland) correlating and integrating body functions such as digestion and reproduction
Simple (SPINAL reflexes)
Nerve impulses travel through THE SPINAL CORD ONLY DO NOT reach the BRAIN
Section 10
(50 cards)
The UPPER Respiratory Tract includes
Nasal Cavity Pharynx which includes: Nasopharynx Oropharynx Laryngopharynx
Heart is a double pump sends blood to
Lungs for OXYGEN through PULMONARY CIRCUIT Remainder of the body through the SYSTEMIC CIRCUIT
Passage ways between the NASAL CAVITIES and the ALVEOLI conduct gases TO & FROM where?
LUNGS
SEMILUNAR VALVES are found where
Entrance PULMONARY TRUNK AORTA
SUPERIOR and INFERIOR VENA CAVAE are the
LARGE VEINS
VEINS are usually
PARALLEL to the ARTERIES Usually have the same name
SYSTEMIC ARTERIES begin with the
AORTA
Internal Respiration refers to the exchange of gases between?
The BLOOD and BODY cells (rmbr: internal = inside = blood & body cells that are INSIDE of the body)
All of the formed elements are produced from where?
Stem cells in RED BONE MARROW
Respiration is CONTROLLED by the respiratory control center in the
MEDULLA of the Brain
The CARDIAC cycle is a period from
The end of one ventricular contraction to the end of the next ventricular contraction
VEINS
Carry blood TOWARD the heart and capillaries
Arterioles
SMALLEST arteries
Platelets are active in the process of
BLOOD CLOTTING
The contraction phases of cycles is
SYSTOLE, which is the CONTRACTION phase and DIASTOLE, which is the RELAXATION phase (rmbr: SC = Systole,Contraction and DR = Diastole,Relaxation)
Vasodilation and Vasoconstriction influence...
Blood pressure Blood distribution to the tissues
VasoCONSTRICTION
CONTRACTION of smooth muscle in the ARTERIAL walls
WHITE BLOOD CELLS, Leukocytes are active
Phagocytosis
Blood is RECEIVED
From the ATRIA
(T/F): Blood serves to transport oxygen and nutrients to body cells and to carry away carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes
TRUE!
The heart has an intrinsic beat initiated by the?
SINOATRIAL NODE and transmitted along a conduction system through the MYOCARDIUM
You can find your heart beat by using
Electrocardiogram, ECG or EKG
The TRICUSPID valve is on the
RIGHT side of the heart (rmbr: TRICUSPID = RIGHT)
Exchanges that take place between the blood and surrounding tissues, exchanging water, nutrients, and waste products happen where?
In CAPILLARIES!
Blood DRAINS from the myocardium into the?
RIGHT ATRIUM through the CORONARY SINUS
Describe the walls of the VEINS
Thinner Less Elastic Carry blood under LOW pressure
As ARTERIES get further and further away from the heart, then become...
Thinner and Thinner
Heart muscles are called?
MYOCARDIUM
The UPPER respiratory tubules?
Lined with CILIA TRAP debris and KEEP FOREIGN SUBSTANCES from ENTERING the LUNGS
EXHALATION is a passive process
LUNGS RECOIL as the RESPIRATORY MUSCLES RELAX THORAX DECREASES size
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Lungs Diaphragm Muscle Surrounding the ribs
The LOWER Respiratory Tract includes
Larynx Trachea Left and Right Primary Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli and everything associated with the alveoli like the: Alveolar Sac Alveolar Duct
UPPER passageways in the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM serve to
Warm filter moisten incoming air
Blood is SUPPLIED to the heart muscles by the?
CORONARY ARTERIES
CAPILLARIES are
The SMALLEST of vessels
Valves are between the
ATRIA and VENTRICLES
Walls of the ARTERIES of the heart
Thick Elastic Carry blood under HIGH pressure
ARTERIES
Carry blood AWAY from the heart (rmbr: ARTERIES = AWAY)
External Respiration refers to the exchange of gases between?
The ATMOSPHERE and the BLOOD through the ALVEOLI (rmbr: external = outside = atmosphere, because the atmosphere is outside)
The SUPERIOR and INFERIOR VENA CAVAE empty into the
RIGHT ATRIUM of the heart
VasoDILATION
RELAXATION of smooth muscle in the ARTERIAL walls
Blood is PUMPED into circulation by
VENTRICLES
The RESPIRATORY SYSTEM supplies
OXYGEN to the body and ELIMINATES CARBON DIOXIDE
AORTA sends
Branches to all parts of the body
ERYTHROCYTES (RBC) are modified for?
Transport of Oxygen
The 5 types of LEUKOCYTES (WBC) can be distinguished on?
Size Appearance of the Nucleus Staining Properties Presence or absence of visible cytoplasmic granules
The BICUSPID valve is on the
LEFT side of the heart
Plasma contains
10% proteins ions nutrients waste hormones DISSOLVED OR SUSPENDED IN WATER
INHALATION
CONTRACTION of the DIAPHRAGM to ENLARGE the THORACIC CAVITY and draw AIR INTO the lungs
The main white blood cells that are involved in Phagocytosis are
Neutrophils and Monocytes
Section 11
(50 cards)
The UNIARY SYSTEM consists of what?
2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra
Amino acids and the simple sugars from protein and carbohydrates being absorbed by?
The BLOOD!
Esophagus
Narrow tube leading From pharynx to the stomach
Most of the fats are absorbed into the lymph by what?
LACTEALS
What is the purpose of the mastication of food
To increase its surface area (Chewing) Increasing the food's surface area promotes easier digestion by letting enzymes get to every portion of it.
Four MAIN LAYERS IN THE DIGESTIVE TRACT from the innermost to the outermost?
Mucous Layer Submucous Layer Muscular Layer Serous Layer
Carbon Dioxide is a regulator of
Blood pH
Bolus
A ball of food that is formed
Saliva is produced by
Three Salivary glands Lubricates Dilutes the chewed food
Alimentary canal consists of what
Mouth Pharynx Epiglottis Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum Anus
3 pairs of salivary glands
Parotid glands- CHEEKS Submandibular glands- FLOOR of the MOUTH Sublingual glands- UNDER the TONGUE
Filtration of the blood occurs through the GLOMERULUS under the force of?
BLOOD PRESSURE
The opening for defecation, or expelling stool is the?
ANUS!
What is the main role of the LARGE INTESTINE?
Reabsorbs water and stores and eliminates undigested food
The URETHRA does what?
PASSES the urine to the OUTSIDE
In the SMALL INTESTINE is where food is acted on by various enzymes
Small intestine and PANCREAS and by the BILE from the LIVER
Abundant bacteria, the intestinal flora is found where?
In the LARGE INTESTINE
The actual filtration process occurs through the ___
GLOMERULUS in the BOWMAN's CAPSULE (aka the glomerular capsule) of the nephron
SOME CARBON DIOXIDE is carried by?
Solution or bound to blood proteins
Salvia contains an enzyme
AMYLASE
Lacteals are eventually added where?
To the bloodstream
MOST CARBON DIOXIDE is converted to?
BI-CARBONATED CARBONIC ANHYDRASE within RED blood cells This reaction also RELEASES: Hydrogen ions and Carbon Dioxide
As the glomerular filtrate passes through the nephron what happens?
The components needed by the body like water, glucose, and ions leave the nephron by diffusion and reenter the blood.
The URTERS are what?
Tubes that TRANSPORT urine to the urinary bladder
Stomach stores food and regulates the movement of food into the
SMALL INTESTINE
Oxygen is released from HEMOGLOBIN as the concentration of OXYGEN...
DROPS in the tissues
Gastric Gland
Hydrochloric acid (HCL) Breaks down foods
The URINARY BLADDER does what?
STORES the the urine
Role of the EPIGLOTTIS
Prevents food from entering the larynx as the food is swallowed
What does the PANCREAS contribute
WATER to dilute the CHYME BICARBONATE IONS to neutralize the acid from the stomach
Food enters ____ first
The stomach
Nephron's role is...
To filter waste material out of the blood brought to the kidneys by the RENAL ARTERY.
Stomach muscle churns and mixes the bolus of food, turning the mass into a SOUPY substance
CHYME!
Digestion and absorption of food occurs where?
In the SMALL INTESTINE
Name the accessory organs of digestion
Liver Pancreas Gallbladder
Alimentary canal
Digestive tube
(T/F): The muscular movements of the stomach and intestines also result in mechanical breakdown of food, thus increasing surface area for digestion
TRUE!
Most oxygen carried in the blood is bound to
HEMOGLOBIN in RED blood cells
What 3 major regions consists of the SMALL INTESTINE?
Duodenum Jejunum Ileum
The KIDNEYS do what?
PRODUCE urine
What are the 5 portions that make up the LARGE INTESTINE?
Ascending Colon Descending Colon Transverse Colon Sigmoid Colon Rectum
All nutrients enter the HEPATIC PORTAL VEIN to be routed where
LIVER for decontamination
Muscles of the pharynx
force/push food into the upper portion of the esophagus food is swallowed through the esophagus
Nutrients are absorbed through the walls of the?
SMALL INTESTINE
Who filters the blood in the body?
THE KIDNEYS
Amylase starts
Digestion of complex carbohydrates
Food is ingested into
MOUTH where it is mechanically broken down by the teeth and tongue through the process of mastication (chewing).
What is the job of the villi
SMALL FINGERLIKE PROJECTIONS that INCREASE the surface area of the intestinal wall
What are the functional units of the KIDNEYS?
The NEPHRON!
What is the shape of a Nephron?
Small coiled tubules
Section 12
(50 cards)
What produces TESTOSTERONE?
The interstitial cells between the seminiferous tubules
During pregnancy, the hormones from the placenta maintain what?
The endometrium Prepare the breast milk production
Thyroid
Metabolism
Role of the CORPUS LUTEUM
Secretes PROGESTERONE and ESTROGEN Stimulates development of the endometrium
FSH regulates what
SPERM PRODUCTION
Eustachian
(middle)Equalizes air Pressure
Macula
Central Vision (yellow)
How is the Reproductive activity in WOMEN?
Cyclic (occurs in cycles)
Approximately day 14 of the cycle
LH is released from the pituitary, which STIMULATES OVULATION and the CONVERSION of the FOLLICLE to the CORPUS LUTEUM
Skeletal Respiratory Circulatory
Acid-Base Balance
Fovea
Clearest Vision/ Focus
Fertilization OCCURS, what happens to the CORPUS LUTEUM
The corpus luteum remains FUNCTIONAL
Ovaries
Estrogen and Progesterone
Antidiuretic Hormone
Regulates water balance
Parathyroid
Calcium and Phosphorus levels
LH stimulates
The intestinal cells to produce testosterone
Each month, under the influence of ___ (hormone) several eggs ripen within the ovarian follicles in the ovary
FSH, Follicle stimulating hormone
Once the sperm is produced what happens?
The sperm is matured and then stored into the epididymis of each testis
Estrogen produced by the follicle initiates (FSH)
The preparation of the endometrium of the uterus for pregnancy Endometrium:It is a MUCOUS membrane in the UTERUS that THICKENS during menstrual cycle in preparation for possible implantation of an embryo
Malleus Incus Stapes (Ossicles)
(inner) Sound Vibration
Along the pathway of ejaculation are what?
Glands that produce the transport medium or semen
In MEN spermatoza develop within the...
Seminiferous tubules of each testis
Testes
Testosterone
Ear Canal/Pinna
(outer ear) secrete wax
Gametes are formed by
MEIOSIS
Endometrium
It is a MUCOUS membrane in the UTERUS that THICKENS during menstrual cycle in preparation for possible implantation of an embryo
The Glands that produce the transport medium or semen includes the?
Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral (Cowper's) Glands
How is the Reproductive activity in MEN?
Continuous (keeps on going, never stops)
Fertilization DOES NOT OCCUR, what happens to the CORPUS LUTEUM?
The corpus luteum DEGENERATES and MENSTRUATION begins
Testosterone, the male hormone influences what?
Sperm cell development Male secondary sex characteristics
During ejaculation the pathway for the sperm includes what?
The Vas Deferens Ejaculatory Duct Urethra
Occipital Lobe
Vision
The fertilized egg or zygote travels where?
To the UTERUS and the developing embryo is nourished by the placenta, which is formed by maternal and embryonic tissues
Testicular activity is under control of 2 ANTERIOR PITUITARY hormones
FSH, which is the Follicle-Stimulating Hormone ICSH, which is the Intestinal Stimulating Hormone OR LH, which is the Lutenizing Hormone
Secondary sex characteristics
Deep voice and Body hair
Fibrous Joints
Tough Collagen fibers
Pineal Gland
Melatonin
What is the final product produced by millions of nephrons per kidney is?
URINE!
Frontal Lobe (Broca's area)
Speech Formation
Corti (Spiral Shape)
(inner) Detect Sound
Pancreas
Healthy blood sugar levels
Adrenal glands
Blood Sugar Control
The egg is only in the oviduct IF
FERTILIZATION OCCURS
(T/F): Water is reabsorbed at the tubules of the nephron?
TRUE!
Temporal lobe
Comprehension Speech (Wernicke's Area) Controlling Auditory
Pituitary Gland
Growth Hormones
AFTER OVULATION, what happens to the eggs?
The egg is swept INTO the oviduct or the fallopian tube
What are the 2 functions of the male and female sex organs?
Production of gametes, or sex cells Production of hormones
The functions of the male and female sex organs take place where?
Under the control of TROPIC hormones from the PIUITARY gland
Gliding Hinge ball socket Saddle
Synovial Joints
Section 13
(50 cards)
Gray Matter
Integrates Retrieves to stimuli
Lens
Light on the back of eye
PNS
Parapsympatetic- Lower heart rate Sympathetic- Fight or flight
Motor Units
Muscle cell
Left Ventricle
aorta-aortic arch
Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Mandible
Jawbone
Lower Leg hold most of weight
Tibia
Smooth Flat Articular
Facet
Mammary Gland
Female Reproductive System
Shallow depression
fossa
Irregular Bone
Vertebrae Sacrum Complex Shape
A bone with a tube-like opening
Meatus
Hyoid
U-Shape (Mandible)
Jejunum
Most Nutrient absorbed
Tendons
Attach to the end of bone
Cerebral
Higher brain Function
Lens
Behind the pupil (Autofocus)
Long Bone (Compact Bone/Spongy Bone)
Arm Leg Support Weight
Visceral Muscle
Blood Vessels
Skeletal muscles
Somatic Nervous System
Rapid Successive Nerve Signal
Tetanos
Gallbladder
Store Bile
Retina
light into electrical impulses
Flat Bone
Skull Thoracic cage Pelvis Protect Internal Organs
heart pump blood
5 Liters per min
Integration
CNS
White Matter
Nerve Signals From brain to body
Fibrous Joints
Tough Collagen Fibers
Rectum
Large Intestine
Pupil
Black-
Femur
thigh bone
Skin
Integumentary System
Thymus
inferior to thyroid
Short Bone
Tarsals (Ankles) Carpals (Wrist) Cube Shape
SInus
Cavity
Iris
Controlling amount of light (Diaphragm of a camera)
Fibula
Muscle attachment of leg
Talus
Foot Seven tarsal bones
Thyroid
Adams Apple
Round hole for blood vessel to pass through
Foramen
Stationary
Origin
Cornea
Clear- Light Focus (Camera Lens)
Myofibrils
muscle contraction
Spleen Thymus
Lymphatic system
Heart
Circulatory system
Body's processin memory regulation
Central Nervous System
Smallest unit of muscle
Sarcomere
Enteric nervous System
function of the digestive organ
Tidal Volume
Amount of Air Shallow breathing
Section 14
(22 cards)